
Bruker has acquired IRM2, a developer of high-speed infrared (IR) imaging microscopes based on quantum cascade laser (QCL) technology. QCL microscopy expands Bruker’s technology portfolio and market opportunities for infrared microscopy, with applications in biological tissue analysis and materials science, and future potential in tissue diagnostics.
QCL is a novel technology in infrared and Raman microscopy, with key customers at academic and government research institutions, as well as in pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. The IRM2 QCL platform provides direct infrared imaging with detector arrays at very high speed. A proprietary coherence reduction technique delivers unprecedented image quality, so that the composition of large sample areas can be studied much more rapidly and at high lateral resolution.






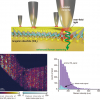

![Targeted proton transfer charge reduction (tPTCR) nano-DESI mass spectrometry imaging of liver tissue from orally dosed rat (Animal 3). a) optical image of a blood vessel within liver tissue. b) Composite ion image of charge-reduced haeme-bound α-globin (7+ and 6+ charge states; m/z 2259.9 and m/z 2636.3 respectively, red) and the charged-reduced [FABP+bezafibrate] complex (7+ and 6+ charge states; m/z 2097.5 and m/z 2446.9 respectively, blue). c) Ion image composed from charge-reduced haeme-bound α-globin (7+ and 6+ charge states) showing abundance in blood vessels. d) Ion image composed from charge-reduced [FABP+bezafibrate] complex (7+ and 6+ charge states) showing abundance in bulk tissue and absence in the blood vessel. Reproduced from https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202202075 under a CC BY licence. Light and mass spectromert imaging of tissue samples](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail/public/news/MSI%20drug-protein%20complex-w.jpg?itok=CBNIjyYl)
