
Canadian company GHGSat, which specialises in high-resolution greenhouse gas monitoring from space, has launched three new ABB-built optical sensors into space, doubling capacity to monitor methane gas emissions. GHGSat’s hyperspectral imaging technology accurately locates and measures methane emissions from any given industrial site on earth. In addition to the three units being launched, five additional units dedicated to methane measurements are under fabrication at ABB.
Space is the only location allowing emissions to be monitored freely across jurisdictions and report on improvements or otherwise. Measuring different sites with the same sensor ensures that emissions are compared consistently. Space measurements are also especially useful for sites where ground sensors are economically not viable or too complex to deploy.






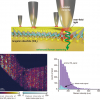

![Targeted proton transfer charge reduction (tPTCR) nano-DESI mass spectrometry imaging of liver tissue from orally dosed rat (Animal 3). a) optical image of a blood vessel within liver tissue. b) Composite ion image of charge-reduced haeme-bound α-globin (7+ and 6+ charge states; m/z 2259.9 and m/z 2636.3 respectively, red) and the charged-reduced [FABP+bezafibrate] complex (7+ and 6+ charge states; m/z 2097.5 and m/z 2446.9 respectively, blue). c) Ion image composed from charge-reduced haeme-bound α-globin (7+ and 6+ charge states) showing abundance in blood vessels. d) Ion image composed from charge-reduced [FABP+bezafibrate] complex (7+ and 6+ charge states) showing abundance in bulk tissue and absence in the blood vessel. Reproduced from https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.202202075 under a CC BY licence. Light and mass spectromert imaging of tissue samples](/sites/default/files/styles/thumbnail/public/news/MSI%20drug-protein%20complex-w.jpg?itok=CBNIjyYl)
