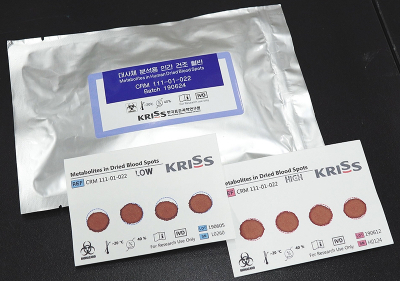
The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) has developed Certified Reference Materials (CRMs) that can enhance the reliability of using dried blood spot testing for newborn screening. DBS is a sample obtained by drying a drop of blood from the finger or heel on a piece of filter paper. This approach is used for screening rather than actual diagnosis, as it is less accurate than venous blood sample tests. Its common applications include newborn screening for inherited metabolic disorders and doping control during Olympics.
The proposed CRM provides eight certified values and 10 reference values for amino acids, glucose, galactose and acylcarnitines, which are diagnostic markers of inherited metabolic disorders in newborns. This allows accurate measurement of the amount of target compounds in the DBS. The lack of reference values has made it difficult for DBS testing to be considered reliable for medical decision. In addition, there has been a problem with measurement bias caused by the need to retrieve portions of blood spots using a paper puncher. The KRISS Biodiagnostics Analysis Team found that a 0.4 mm bias in diameter led to a 0.78 μL difference in sample volume. The research team controlled the sample volume to 50 μL during the CRM manufacturing stage, and proposed bias-free measurements as certified values, thereby successfully creating CRMs with complete measurement traceability to the International System of Units. This is the first-ever development of DBS CRMs.
KRISS plans to develop more CRMs for other diagnostic markers used in newborn screening.