Imaging News
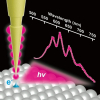
The presence of kaolinite haloes surrounding ancient fossils is believed to have kept destructive bacteria at bay, stopping decay. The small molecular differences of the clay were analysed with the synchrotron infrared microbeam at Diamond Light Source.
A new type of imaging system for use in agriculture, designed to be far less expensive than existing technology, is being developed in a partnership between Scottish academics and industry.
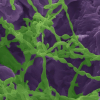
Electron microscopy and Raman spectroscopy have shown the mechanism by which microorganisms are able to extract water from the rocks they colonise.
Using a smartphone camera and spectral super-resolution spectroscopy, anaemia and blood disorders can be assessed outside the lab.
Every year, the WITec Paper Award competition recognises three exceptional peer-reviewed publications that feature results acquired with a WITec microscope.The 2020 Paper Awards go to researchers from Japan, Poland and Austria.
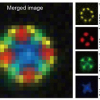
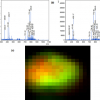
Using gas cluster ion beam secondary ion mass spectrometry (GCIB-SIMS), researchers at Penn State have directly observed functional enzyme clusters (metabolons) involved in generating purines, the most abundant cellular metabolites.
Applications are invited for these prestigious awards administered by the Association of British Spectroscopists (ABS) Trust.
A team of researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Applied Optics and Precision Engineering IOF in Jena has developed a quantum imaging solution that can produce detailed insights into tissue samples using extreme spectral ranges and less light.
Using cryogenic, ultrahigh-vacuum TERS and fine-tuning the highly localised plasmon field at the sharp tip apex has reduced the spatial resolution to 1.5 Å
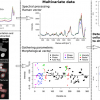
Metabolic diseases such as diabetes and obesity are ever more common globally. In addition to genetic disposition, lifestyle contributes strongly to their prevalence. Precise monitoring methods are needed in order to, for example, evaluate how a change in diet or exercise affects disease and its metabolic characteristics.
Headwall BVBA, Belgium and geo-konzept of Germany have announced the formation of a Centre for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Europe (CHRSE).
Quantitative phase microscopy and Raman spectroscopy provide a label-free way to extract biomarkers based on cellular morphology and intracellular content.
Scientists at Münster University use dual-beam lasers to increase the resolution of MALDI MS imaging.
Shimadzu has opened a branch office in Sweden, which will market Shimadzu’s full range of analytical instrumentation solutions.
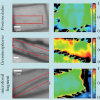
XRF mapping, infrared and hyperspectral imaging reveal early designs for Leonardo da Vinci’s The Virgin of the Rocks.
By being resident on-site at a hydrothermal vent for 12 months, InVADER will capture transient events and provide unprecedented spatial and temporal access to a deep ocean hydrothermal system.
The new matrix-assisted ionisation in vacuum (MAIV) technique has been used to generate mass spectrometry images for the first time. The technique’s ability to generate multiply charged ions from peptides and proteins facilitates their identification by tandem mass spectrometry.
A step forward toward achieving nanoscale imaging and spectroscopy with tailored “nanolight”.
Young scientists can apply for laboratory bench space for their own research in “Shimadzu Laboratory World”.
Danish researchers have developed a high-resolution imaging method that can capture mid-infrared spectral images on the order of milliseconds.