Raman Spectroscopy News
Using ultrashort pulsed laser technology, infrared and Raman spectroscopy can be performed simultaneously.
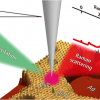
Tip-enhanced “resonance” Raman scattering can be used to investigate a specific chemical structure at nanoscale and even at the single-molecule level, and also provides a new approach for the atomic-scale optical characterisation of local electronic states.
Shimadzu has opened a branch office in Sweden, which will market Shimadzu’s full range of analytical instrumentation solutions.
The technique can identify cancerous thyroid cells with 97 % accuracy, and also showed that subtypes could be identified by their spectral differences.
By being resident on-site at a hydrothermal vent for 12 months, InVADER will capture transient events and provide unprecedented spatial and temporal access to a deep ocean hydrothermal system.
Nominations for the 2019 Norman Sheppard Award are invited.
The ABS Trust is seeking applications for the Gordon F. Kirkbright bursary award and the new Edward Steers bursary, both open to early career scientists.
imec have developed an on-chip solution for Raman spectroscopy that could be used to manufacture high-performance, handheld Raman devices; perhaps even in smartphones.
Timegate Instruments, manufacturer of time-gated Raman spectroscopy instruments, has raised funding of 2.6 M€ for product and business development.
At the IRDG Christmas Meeting held at University College London, the 2018 Norman Sheppard Award of the UK’s IRDG was presented to John Chalmers.
The winner of this award from the UK’s Infrared and Raman Discussion Group is John Chalmers, who was Article Editor for Spectroscopy Europe for many years.
Tornado’s Raman spectroscopy system has won in the category, “Excellence in Pharma: Analysis, Testing, and Quality Control”.
Research has shown that Raman spectroscopy predicted glucose values as accurately as a finger prick test.
Machine learning techniques using a combination of the layer clustering and decision tree methods aids prediction of spectra.
PhD students worldwide who have defended their thesis in the last two years are invited to apply for this award.
A rare mineral that holds potential as a new material for industrial and medical applications has been discovered on alpine plants by Raman microscopy.
Using spectroscopic techniques including Raman and XANES, 3.4 billion year old microfossils from Western Australia’s Strelley Pool formation have been shown to be chemically similar to modern bacteria. This all but confirms the biological origins of the fossils and ranks them among the world’s oldest.
Metrohm AG has acquired B&W Tek’s Spectroscopy Solution business, B&W Tek LLC, as well as several overseas subsidiaries.
Princeton Instruments and the Center for Structured Organic Particulate Systems (C-SOPS) have announced a six-month collaboration on the use of Raman spectroscopy to monitor and control drug manufacturing processes.
Applications for this prestigious award are invited by 30 November 2018.